Applying Automatic Testing in the Development Cycle
Background
Testing is a critical aspect of any software development process. Ensuring that an application functions as expected and is free of defects is essential for delivering a high-quality product to end-users. In this section, we will discuss the importance of testing in the development cycle and highlight the benefits of automating this process.
Testing is an integral part of the production process, and it is crucial to remember that your software will be tested eventually, whether by you, your automated testing scripts, or the end-user. Neglecting to test a product thoroughly can result in subpar performance, errors, and, ultimately, dissatisfied customers.
Most testing tasks are simple and repetitive, making them excellent for automation. By automating testing processes, you can save valuable time and resources, improve accuracy, and reduce the likelihood of human error(Alway bear in mind that Humans are not prefect, they make a lot of stupid mistakes). Automated testing can also be run as frequently as needed, ensuring that defects are identified and addressed promptly.
Throughout the development cycle, various types of testing should be implemented to catch bugs and issues as early as possible, making them easier to resolve. By incorporating different testing techniques, such as unit testing and end-to-end (E2E) testing, you can ensure that your application is thoroughly vetted at every stage of development. In the following sections, we will explore the standard development cycle and discuss how to apply automated testing effectively within this framework.
Development Cycle
A standard agile workflow for the software development lifecycle (SDLC) typically consists of several stages, each with its purpose and goals. These stages include:
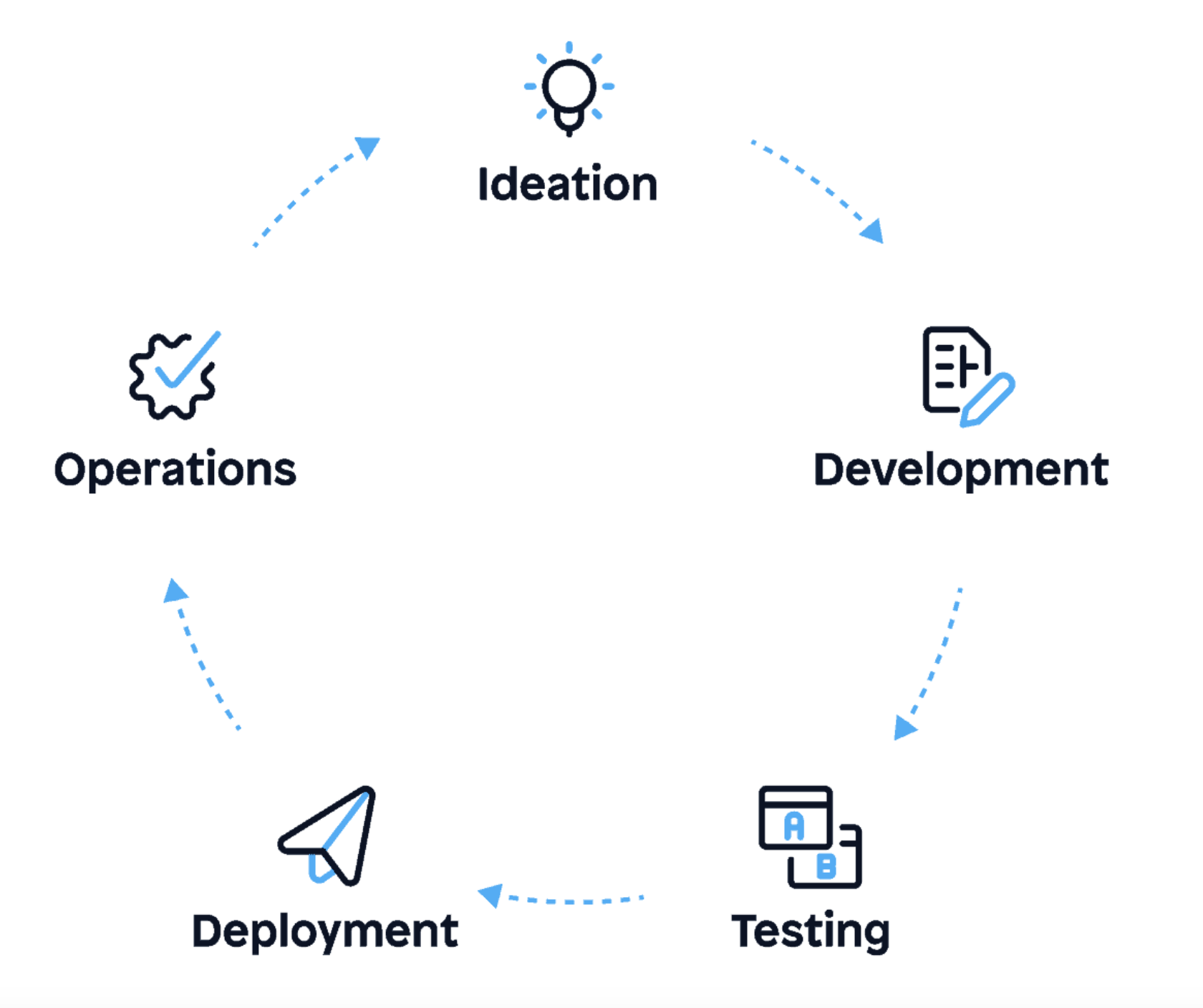
- Ideation: This phase involves generating ideas, identifying opportunities, and defining the project’s goals and requirements.
- Development: This includes UX/UI, architecting design, coding, integrating.
- Testing: This phase involves verifying the software’s functionality, performance, and overall quality.
- Deployment: In this stage, the software is released to a production environment gradually.
- Operations: The final phase involves maintaining and updating the software as needed, addressing any issues that arise, and continuously improving the product based on user feedback and performance metrics.
Different companies may have unique variations of the SDLC, tailored to their specific needs and workflows. In my team, our SDLC follows this structure:
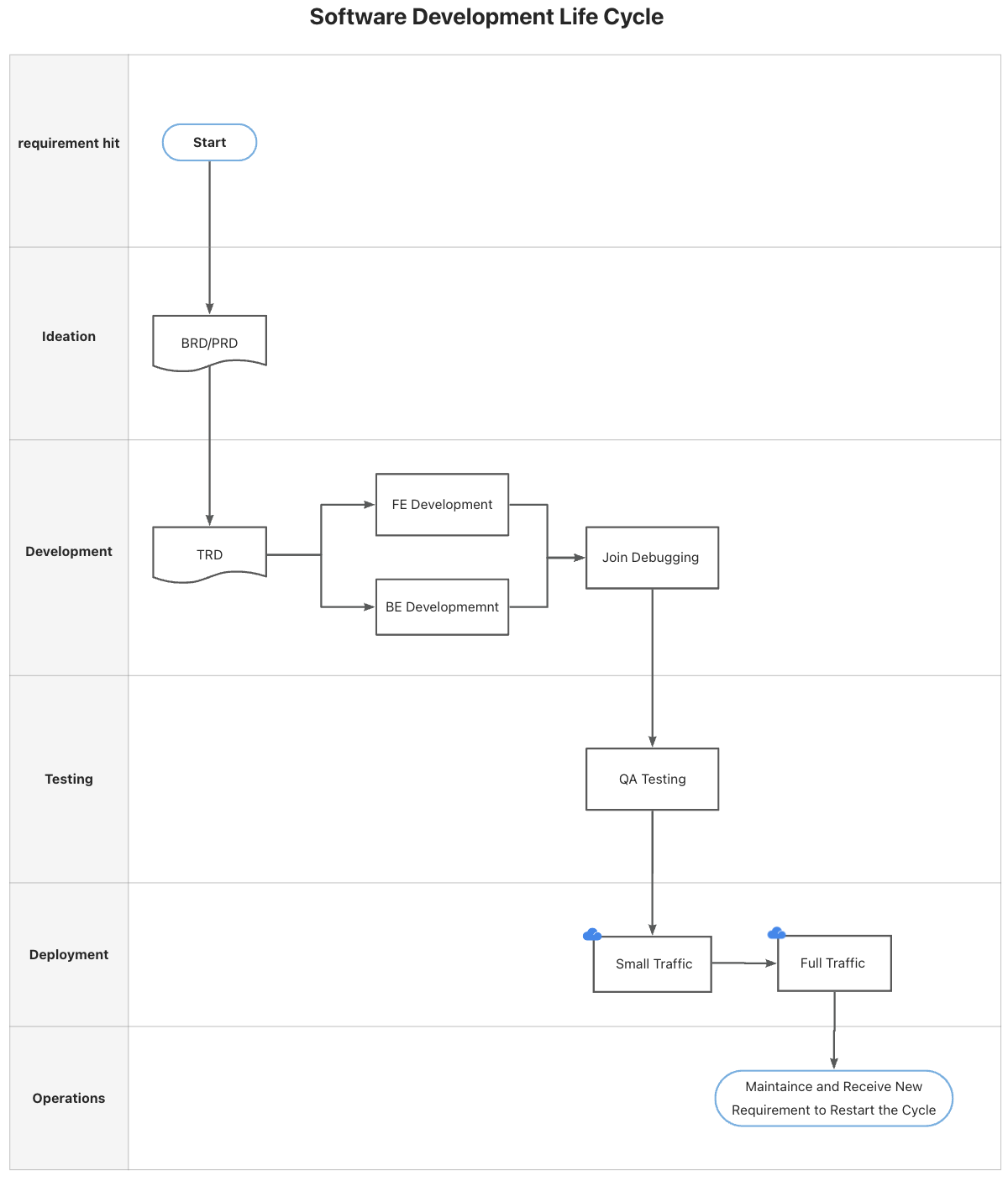
- Write BRD/PRD (Business Requirements Document/Product Requirements Document): These documents outline the project’s goals, objectives, and requirements. They serve as the foundation for subsequent stages of development.
- PRD Review: Team members(Including Developer) review the PRD to ensure the design is reasonable from both user and developer’s point of view.
- Write TRD (Technical Requirements Document): This document outlines the technical specifications and architecture of the software, detailing how the product requirements will be implemented.
- TRD Review: The technical requirements are reviewed by relevant stakeholders, ensuring that the proposed solution aligns with the project’s goals and constraints.
- Implementation (Front-end/Back-end): Developers begin coding the application, focusing on both front-end and back-end components.
- Code Review: Other team members review the code to ensure it adheres to best practices and meets the project requirements.
- Refactoring: Any necessary changes or improvements to the code are made during this stage.
- QA Testing: Quality assurance testing is conducted, including manual and automated tests, to ensure the software meets the desired quality standards.
- Small Traffic: The application is gradually rolled to a small group of users, closely monitoring performance and user feedback.
- Full Traffic: The software is finally deployed to all intended users, marking the completion of the development cycle.
- Maintenance: There isn’t any prefect system in the world, and the requirement is changing. So we need to frequently maintain and iterate our system.
The Limitations of Manual Testing
Although the development cycle can produce quality products, my team still encounters occasional bugs and incidents, some of which are my own responsibility. In March 2023, we experienced five incidents, and while none were severe, they highlighted the need for improvement. Human error is inevitable, which is why automation is essential. Let’s examine some specific problems in my team’s incidents.
Code Changes and QA Testing Overlap
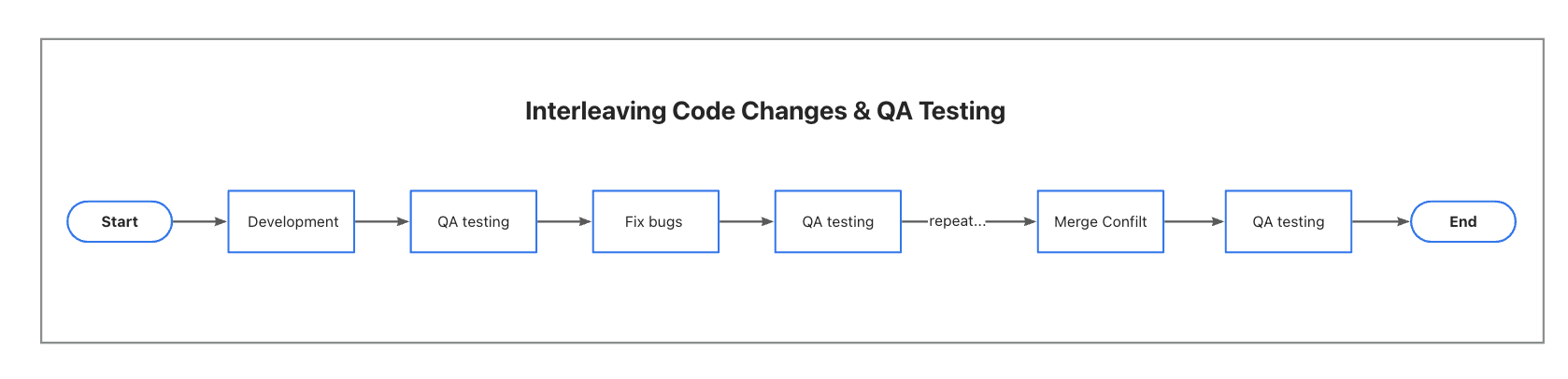
Ideally, testing should always follow code changes. However, in practice, this isn’t always feasible. After the QA testing phase, developers must fix bugs, resolve conflicts when merging code, and more. With only manual testing, the process becomes time-consuming and resource-intensive, making it impractical to perform thorough QA testing repeatedly.
Consider this example from my team’s incidents:
- Merging conflicts led to a missing route: Rapid product iterations and simultaneous requirements led to frequent conflict resolution. Resolving conflicts can introduce bugs, especially when the person handling the conflict only write part of the code. Focusing manual testing on the requirements themselves allows such incidents to occur.
Dependency on Black Box Modules
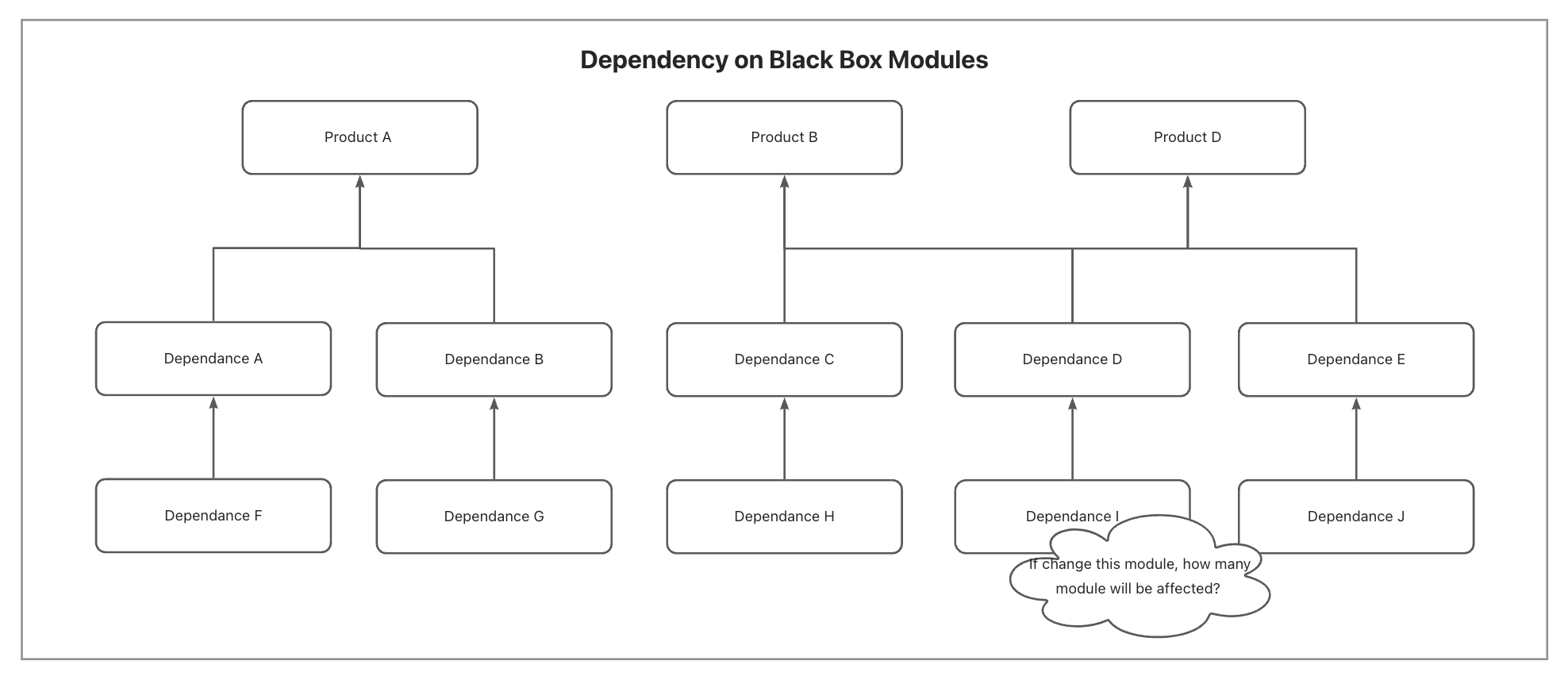
Our systems heavily depend on numerous external dependencies. Modularity is crucial for building complex systems, but it often means relying on black box modules. Trusting these dependencies can lead to bugs.
Consider these incidents:
- Dependency changes caused a product entrance to disappear: Developers may not be aware of the impact their changes have on downstream products. It isn’t practical to have QA manually test all downstream products when a dependency changes.
- Outdated JS Bridge (JSB) documentation led to malfunctioning features in some app versions: It’s unreasonable to expect developers or QA to test every app version when developing a new feature that uses JSB. Developers trust documentation, but when it’s outdated, incidents can occur.
Combinatorial Explosion
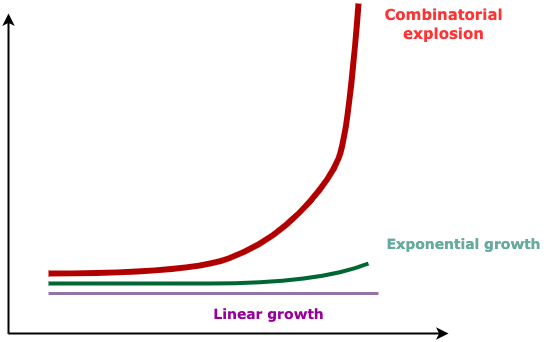
Our team serves global users across various regions, languages, platforms, and app versions. Features also have multiple combinations. The number of possible combinations O(m^n) (A * B * C * D …) is enormous, and most are repetitive. Humans are not well-suited for this task, as demonstrated by this incident:
- A feature was missing in some regions: Our team released a feature across multiple regions, but it was missing in some regions for a month. The simple reason was that no one tested it in those regions. It’s impractical to expect QA to test every region individually for each requirement.
Applying Automatic Testing in SDLC
One of the keys to enhancing software development agility is automation. Considering the limitations of manual testing, we know that manual work is time-consuming and prone to error. Thus, we need to incorporate automatic testing in our SDLC. In this section, I will introduce how to apply various types of automatic testing into SDLC and demonstrate their effectiveness in preventing incidents and bugs in our products.
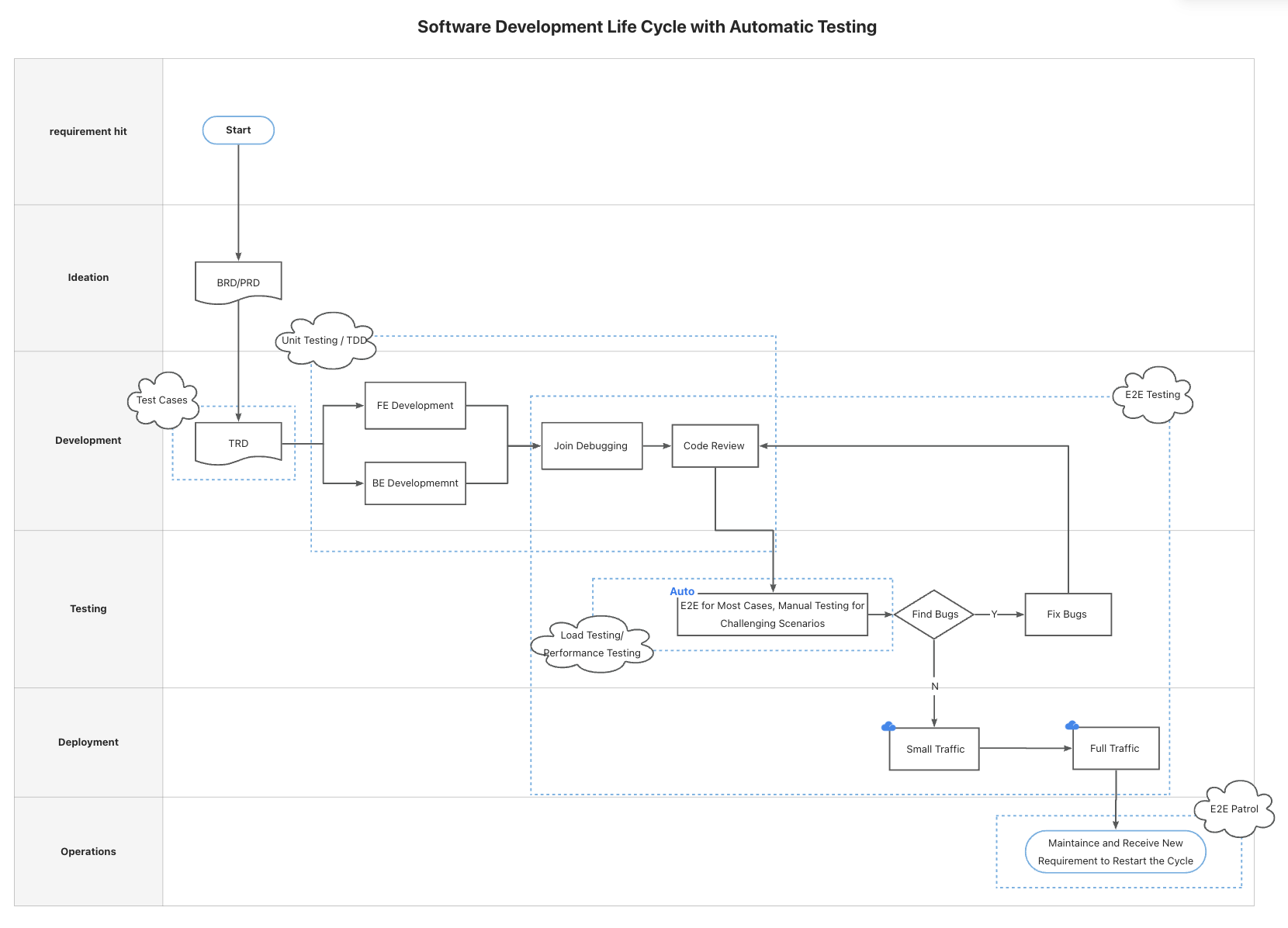
TRD: Writing & Reviewing Test Cases
During the TRD phase, it’s crucial to document test cases for each new module and have them reviewed by other developers. With the introduction of automated testing, test cases provide an excellent way to describe user interactions with our modules. Test cases might look like: “It should display something when the user clicks something,” or “It should return something when inputting something.” They describe how users (end-users or developers) interact with the modules, serving as documentation in our codebase for maintainability.
Development: Unit Testing & TDD
During development, we create test scripts for individual units and strive to pass each test case. These tests act as our first users of the modules. Writing unit tests offers numerous benefits, such as isolating problems, simplifying troubleshooting, testing boundary cases, and reusing existing tests to ensure we don’t accidentally break anything. By adopting Test-Driven Development (TDD), you can reap even more benefits from unit testing. Check out my blog posts on How Testing Speeds Up Your Development and Testing Best Practice Tdd for more information.
Integration & Testing: E2E Testing
Once we’ve completed both front-end and back-end development, we can initiate end-to-end (E2E) testing. By automating manual testing, we significantly reduce the complexity of QA testing. Additionally, we can reuse our previous test cases for regression testing. This allows developers to confidently modify code and resolve conflicts, knowing that E2E tests will follow their changes and ensure the overall integrity of the application.
Patrol, Load Testing, Performance Testing, and More
We can set up E2E testing patrols for our production environment to detect issues as quickly as possible, rather than waiting for user feedback. By implementing load testing and performance testing, we can assess our product’s quality from various perspectives, ensuring a more robust and reliable end product.
Conclusion
In summary, incorporating automatic testing into the development cycle can significantly reduce development time while improving reliability, maintainability, and scalability. By implementing these testing methods, the majority of incidents above can be prevented, leading to a more agile and efficient SDLC. Applying automatic testing as a vital part of the development process results in higher quality products and a smoother experience for both developers and end-users.
agile, sdlc, software engineering, testing — Apr 1, 2023
Made with ❤ and at Earth.